Forschung
Diese Seite ist leider noch nicht auf Deutsch verfügbar.
From Protein Machineries to Function
Perception, processing and storage of information (memory formation) occurs through signaling at and across the plasma membrane.
Our central goal is comprehensive understanding of the molecular principles of the organization and operation of this signaling under normal and disease conditions and its implication for physiology and pathophysiology.
We use a multi-disciplinary approach on several model systems to explore
- how trans-membrane signaling is organized by proteins and protein-assemblies in native systems (high-resolution proteomics)
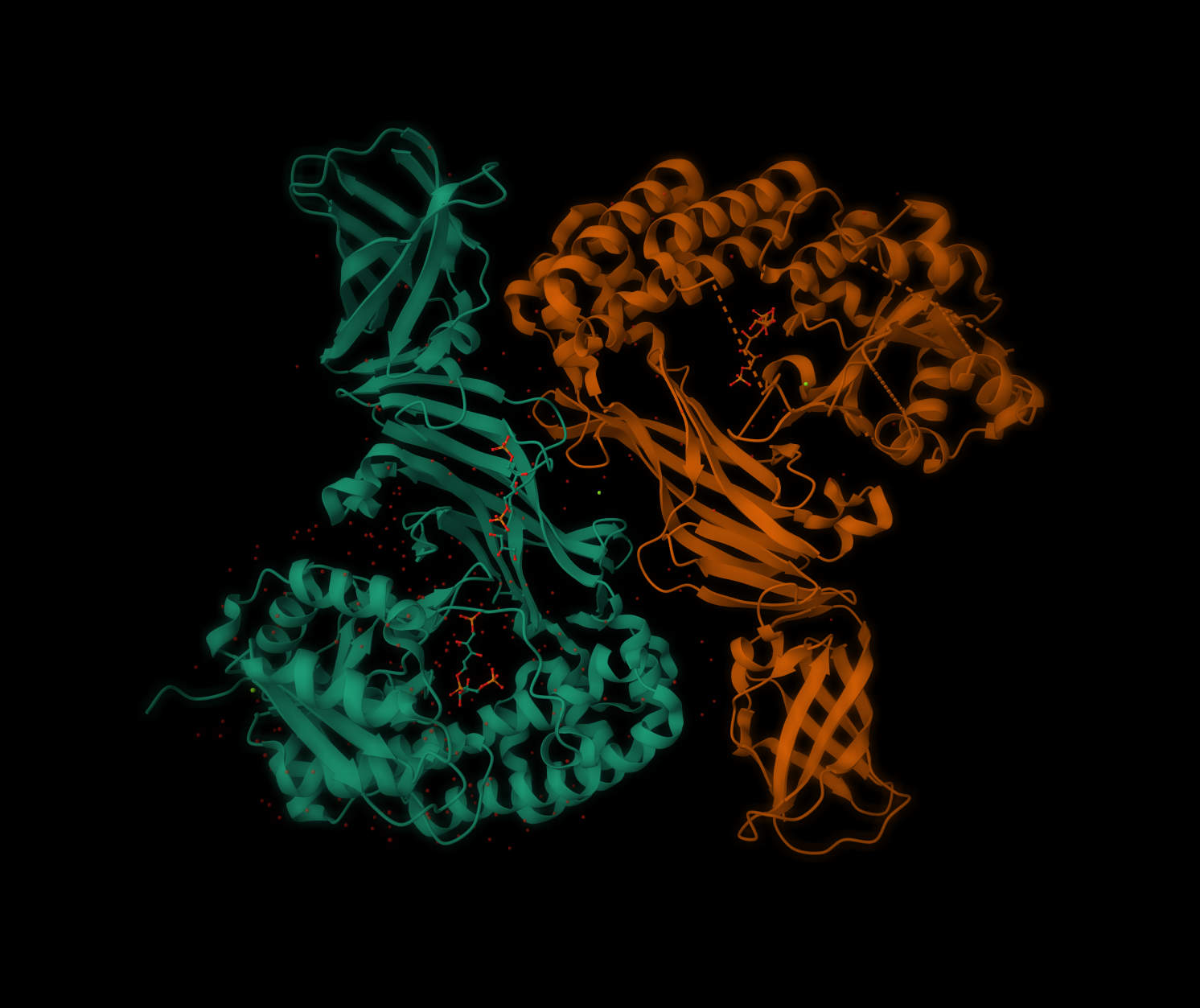
- how these assemblies are operated by protein-protein interactions (structure-function analyses)
- how these assemblies are dynamically shaped by activity (dynamics of protein complexes/machineries)
- how assemblies co-operate in networks to determine function and its specificity in time and space (protein networks and systems).
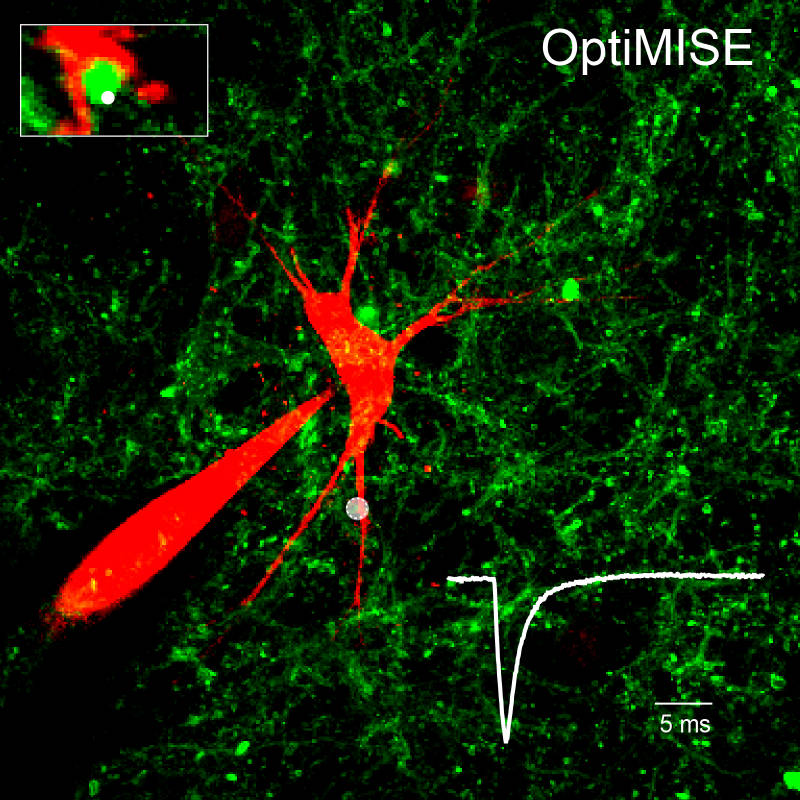
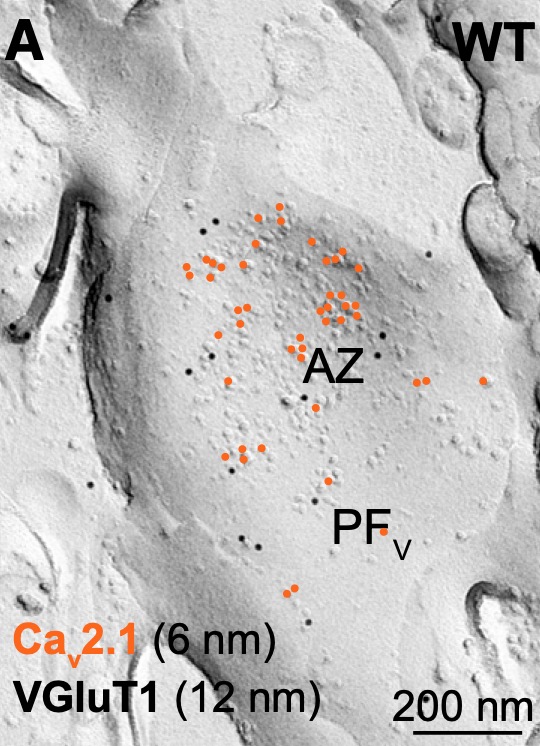

Model Systems
Ion channels
Key elements of rapid signal transduction in the milliseconds-range, promote ion flux across the cell membrane upon activation by voltage and/or ligands.
Types: Glutamate receptors (AMPA-type), GABAA receptors, voltage-gated calcium channels, TRPC channels, BK-type calcium-activated potassium channels
G-protein-coupled receptors
Key elements of signal transduction in the range of several hundred ms to seconds, drive cellular processes via trimeric G-proteins and various effector proteins (adenylate cyclase, phospholipase C, ion channels).
Types: GABAB receptors, metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs)
Transporters
Key players of cellular homeostasis in any type of cell, by shuffling ions along or against concentration gradients.
Types: Calcium-pumps of the plasma membrane (PMCA), sodium-phosphate transporter (NaPiII)
Cell adhesion proteins
Central elements for generation and organization of the cell-cell junctions underlying communication between neurons in the brains (synapses) or between epithelial cells.
Types: Neurexin-T178-PTPR modules, renal slight-diaphragm
Publications
Selected Journal Articles

Mitochondrial complexome reveals quality-control pathways of protein import.
Schulte U, den Brave F, Haupt A, Gupta A, Song J, Muller CS, Engelke J, Mishra S, Martensson C, Ellenrieder L et al.
Nature 2023

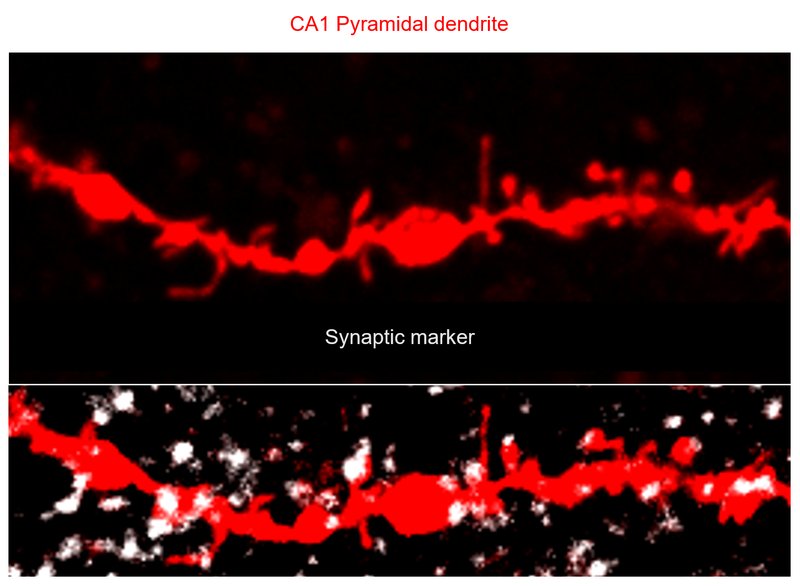
Noelin-organized extracellular network of proteins required for constitutive and context-dependent anchoring of AMPA-receptors.
Boudkkazi S, Schwenk J, Nakaya N, Brechet A, Kollewe A, Harada H, Bildl W, Kulik A, Dong L, Sultana A et al.
Neuron 2023

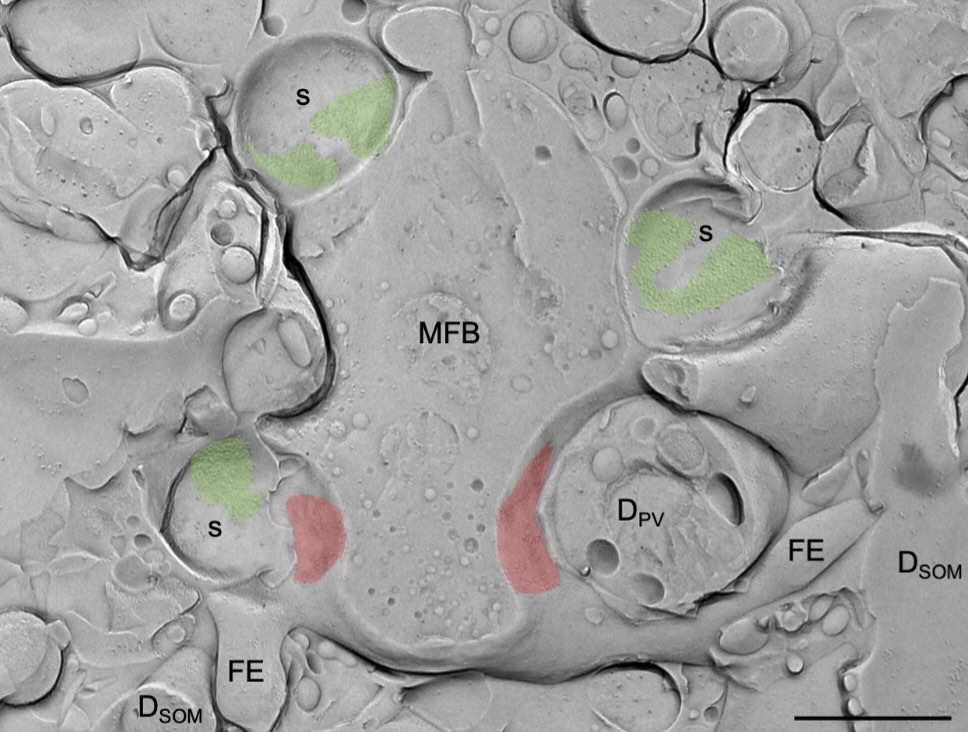
Subunit composition, molecular environment, and activation of native TRPC channels encoded by their interactomes.
Kollewe A, Schwarz Y, Oleinikov K, Raza A, Haupt A, Wartenberg P, Wyatt A, Boehm U, Ectors F, Bildl W et al.
Neuron 2022

An ER assembly line of AMPA-receptors controls excitatory neurotransmission and its plasticity.
Schwenk J, Boudkkazi S, Kocylowski MK, Brechet A, Zolles G, Bus T, Costa K, Kollewe A, Jordan J, Bank J et al.
Neuron 2019

Neuroplastin and Basigin are essential auxiliary subunits of plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPases and key regulators of Ca2+ clearance.
Schmidt N, Kollewe A, Constantin CE, Henrich S, Ritzau-Jost A, Bildl W, Saalbach A, Hallermann S, Kulik A, Fakler B et al.
Neuron 2017

High-resolution proteomics unravel architecture and molecular diversity of native AMPA receptor complexes.
Schwenk J, Harmel N, Brechet A, Zolles G, Berkefeld H, Muller CS, Bildl W, Baehrens D, Huber B, Kulik A et al.
Neuron 2012

Native GABA(B) receptors are heteromultimers with a family of auxiliary subunits.
Schwenk J, Metz M, Zolles G, Turecek R, Fritzius T, Bildl W, Tarusawa E, Kulik A, Unger A, Ivankova K et al.
Nature 2010

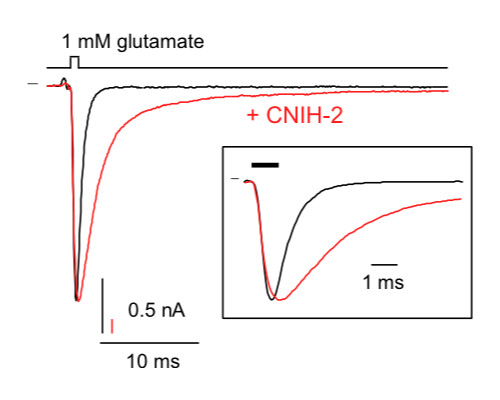
Functional proteomics identify cornichon proteins as auxiliary subunits of AMPA receptors.
Schwenk J, Harmel N, Zolles G, Bildl W, Kulik A, Heimrich B, Chisaka O, Jonas P, Schulte U, Fakler B et al.
Science 2009